How to Resolve TPM Device Not Detected Error – Easy Solutions

The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a security feature embedded in modern computers that provides hardware-based security functions. However, users sometimes encounter a “TPM Device Not Detected” error, especially when trying to install or upgrade to Windows 11, which requires TPM 2.0. This error can be frustrating, but it is usually easy to resolve. In this guide, we’ll walk you through simple steps to fix the “TPM Device Not Detected” error, ensuring your system meets security and compatibility requirements.
1. What is a TPM Device and Why is it Important?
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized chip on a computer’s motherboard that provides a secure environment for sensitive data like encryption keys, passwords, and digital certificates. TPM enhances system security by providing hardware-based protection against unauthorized access.
Key Functions of TPM:
- Encryption Key Storage: Safely stores cryptographic keys and other sensitive data.
- Secure Boot: Ensures the system boots only with trusted software.
- Windows Hello and BitLocker: Supports Windows features like Hello (biometric login) and BitLocker (drive encryption).
Understanding the importance of TPM helps recognize why resolving the “TPM Device Not Detected” error is crucial for system security and functionality.
2. Common Causes of the “TPM Device Not Detected” Error
The “TPM Device Not Detected” error can occur for several reasons:
- TPM Disabled in BIOS/UEFI: The TPM is disabled in the BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Outdated BIOS/UEFI Firmware: The system firmware is outdated and doesn’t recognize the TPM.
- Corrupted or Missing TPM Drivers: TPM drivers are missing or corrupted.
- Hardware Compatibility Issues: The computer does not have a TPM chip, or it’s not compatible with the required version (e.g., TPM 2.0 for Windows 11).
Identifying the cause will guide you toward the appropriate solution.
3. How to Fix the “TPM Device Not Detected” Error
Here are simple steps to resolve the “TPM Device Not Detected” error.
Step 1: Enable TPM in BIOS/UEFI Settings
Often, the TPM is disabled by default in the BIOS/UEFI settings. Enabling it can solve the issue.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Restart Your Computer and Enter BIOS/UEFI:
- Restart your PC and press the BIOS/UEFI key (usually F2, F10, Delete, or Esc) during the startup process.
- Navigate to the Security or Advanced Settings:
- Use the arrow keys to navigate to the “Security” or “Advanced” tab in the BIOS/UEFI menu.
- Locate TPM Settings:
- Look for “TPM,” “Intel Platform Trust Technology (PTT),” or “AMD fTPM” settings, depending on your CPU.
- Enable TPM:
- Select the TPM setting and choose “Enable.”
- Save and Exit BIOS/UEFI:
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI settings (usually by pressing F10).
- Restart Your Computer:
- Allow your computer to restart normally. Check if the error is resolved.
Step 2: Update BIOS/UEFI Firmware

An outdated BIOS/UEFI firmware may not support TPM. Updating the firmware can help resolve the error.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Identify Your Motherboard Manufacturer and Model:
- Find out your motherboard manufacturer and model by checking your PC documentation or the system information.
- Visit the Manufacturer’s Website:
- Go to the official website of your motherboard or laptop manufacturer.
- Download the Latest BIOS/UEFI Update:
- Navigate to the “Support” or “Downloads” section and download the latest BIOS/UEFI firmware update.
- Follow the Update Instructions:
- Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions to update your BIOS/UEFI firmware.
- Restart Your Computer:
- Restart your computer and check if the TPM device is now detected.
Step 3: Update or Reinstall TPM Drivers
Corrupted or missing TPM drivers can cause detection issues. Updating or reinstalling these drivers may resolve the problem.
Step-by-Step Guide:
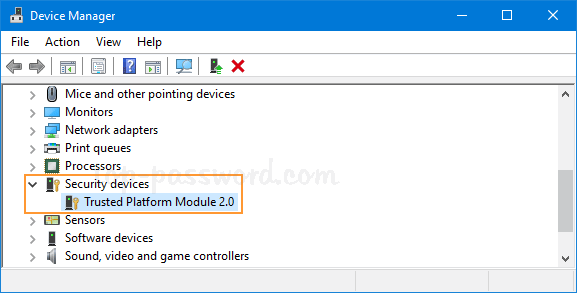
- Open Device Manager:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- Expand the ‘Security Devices’ Section:
- Look for “Security devices” and expand the section.
- Right-Click on ‘Trusted Platform Module’:
- Right-click on “Trusted Platform Module” and select “Update driver.”
- Choose ‘Search Automatically for Drivers’:
- Select “Search automatically for drivers” to let Windows find and install the latest drivers.
- Restart Your Computer:
- Restart your computer to apply the changes and check if the TPM device is detected.
Step 4: Clear the TPM
If the TPM is detected but not functioning properly, clearing the TPM can reset it to a working state.
Step-by-Step Guide:
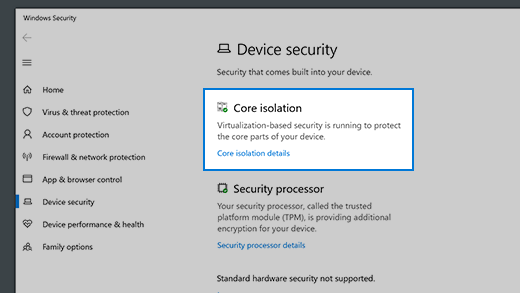
- Open Windows Security:
- Go to the Start menu and open “Windows Security.”
- Navigate to ‘Device Security’:
- Click on “Device security” and select “Security processor details.”
- Click on ‘Security processor troubleshooting’:
- Click on “Security processor troubleshooting” and then “Clear TPM.”
- Restart Your Computer:
- Restart your computer and follow the on-screen instructions to clear the TPM.
- Check TPM Status:
- After restarting, check if the TPM device is now functioning correctly.
4. Best Practices for Managing TPM and System Security
To maintain TPM functionality and enhance system security, follow these best practices:
- Keep BIOS/UEFI and Drivers Updated: Regularly check for updates to ensure compatibility and security.
- Enable TPM Only When Needed: If not required, consider keeping TPM disabled to avoid potential vulnerabilities.
- Use Trusted Security Software: Employ reliable antivirus and security software to protect your system.
- Backup Important Data: Regularly back up your data to protect against potential data loss during troubleshooting or updates.
Conclusion
The “TPM Device Not Detected” error can prevent you from accessing key security features or upgrading to newer versions of Windows. However, by following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily resolve the error and ensure your system’s security and compatibility.
Whether it’s enabling TPM in BIOS, updating firmware, or reinstalling drivers, these simple steps will help you fix the issue and restore full functionality to your TPM device. For more advanced troubleshooting, consider consulting with your system manufacturer or visiting the official Microsoft support website for additional resources.
