How to Resolve High Network Usage and Memory Leaks Caused by svchost.exe (netsvcs)
The svchost.exe (netsvcs) process in Windows manages several essential services, often linked to network functions. However, some users experience issues where svchost.exe (netsvcs) consumes unusually high amounts of memory and network resources, leading to slower performance. This guide will walk you through various troubleshooting methods to reduce network and memory usage caused by svchost.exe (netsvcs).
Understanding svchost.exe (netsvcs)
The svchost.exe process, short for “Service Host,” runs multiple Windows services in the background. When Windows uses this process to host network-related services (netsvcs), it can sometimes encounter memory or network leaks, especially after an update or due to malware.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix High Network Usage and Memory Leak
1. Restart Windows Update Service
The Windows Update service can sometimes cause svchost.exe to use excessive resources. Restarting this service can help.
- Open Run Window: Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type “services.msc”: Press Enter to open the Services window.
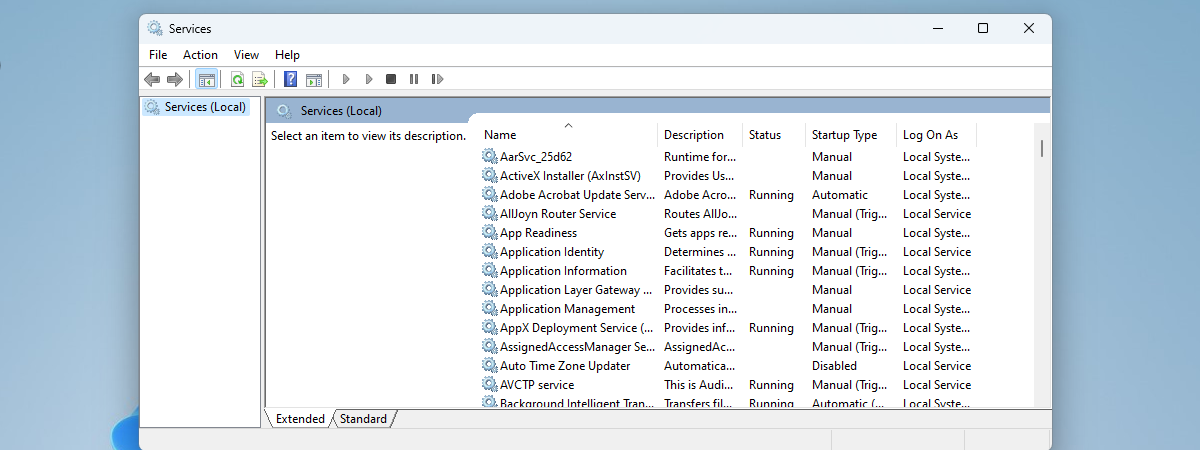
- Locate Windows Update: Scroll down to find Windows Update.
- Restart the Service: Right-click Windows Update and select Restart.
Restarting the service can resolve temporary memory leaks or network usage issues caused by updates.
2. Disable the Windows Update Service (Temporary Solution)
If the high memory usage is persistent, you may need to temporarily disable the Windows Update service.
- Open Services: Go to Run (Win + R) and type services.msc.
- Find Windows Update: Right-click Windows Update and choose Properties.
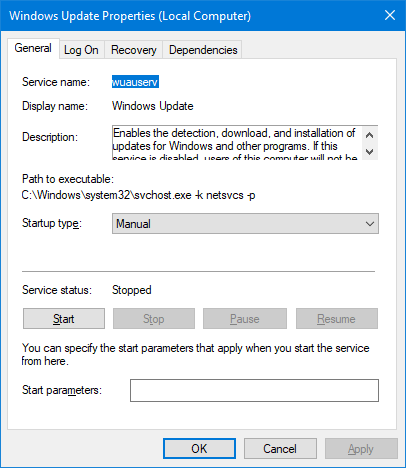
- Set Startup Type to “Disabled”: Under the Startup type dropdown, select Disabled.
- Click Stop and Apply: Select Stop, then click Apply and OK.
Note: Disabling updates isn’t a permanent solution and is not recommended long-term, as updates improve system security.
3. Scan for Malware and Viruses
Malware can disguise itself as svchost.exe and lead to high network and memory usage.
- Open Windows Security: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection.
- Run a Full Scan: Select Scan options, then choose Full scan and click Scan now.
- Check for Threats: Follow the prompts to remove any malware detected.
Using an external antivirus software to scan your system can also help if Windows Defender doesn’t detect anything.
4. Limit Background Applications Using Network Resources
Too many background apps using network resources can contribute to high network usage.
- Open Settings: Press Win + I and go to Privacy.

- Select Background Apps: In the left panel, click Background apps.
- Toggle Off Background Apps: Toggle off the switch for unnecessary apps that use network resources in the background.
This will reduce network usage by limiting apps that run in the background.
5. Use Resource Monitor to Identify Specific Services
You can use Resource Monitor to see which services under svchost.exe are using the most memory or network.
- Open Resource Monitor: Press Win + R, type resmon and hit Enter.

- Go to Network Tab: Switch to the Network tab to view network usage by process.
- Identify High Usage by svchost.exe: Look for svchost.exe processes with high network usage. Right-click and select Analyze wait chain if it seems unresponsive.
Disabling specific services may reduce network usage, but only disable services you recognize and don’t need.
6. Check for Windows Update Bugs and Hotfixes
Some high memory usage issues arise after specific Windows updates, which may require hotfixes.
- Check for Updates: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Install Available Hotfixes: If a hotfix for svchost.exe issues is available, install it.
7. Adjust Virtual Memory Settings
Increasing the size of your virtual memory may alleviate memory leaks temporarily.
- Open System Settings: Right-click This PC, select Properties, then go to Advanced system settings.
- Open Performance Options: In the Advanced tab, select Settings under Performance.
- Increase Virtual Memory: Go to the Advanced tab and click Change under Virtual Memory. Adjust it to a larger size if needed.
8. Reset the Network Configuration
Resetting the network can clear any cache-related issues that cause high network usage.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Type cmd in the search bar, right-click Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator.
- Enter Network Reset Commands:
Restart your computer after entering these commands.
9. Update or Roll Back Network Drivers
Outdated network drivers can cause issues with svchost.exe.
- Open Device Manager: Right-click Start and select Device Manager.
- Update Network Adapter: Expand Network adapters, right-click your network device, and select Update driver.
If a recent update caused issues, consider rolling back the driver to a previous version.
10. Disable Diagnostics Policy Service
The Diagnostics Policy Service is occasionally linked to high memory usage.
- Open Services: Use Win + R, type services.msc, and press Enter.
- Disable Diagnostics Policy Service: Locate Diagnostics Policy Service, right-click it, and select Stop.
- Set to Disabled: Right-click again, go to Properties, and set the Startup type to Disabled.
Conclusion
High network and memory usage caused by svchost.exe (netsvcs) can slow down your system, but following these steps should help reduce its impact. Restarting services, managing background applications, and updating drivers are effective solutions for managing resource usage. Keep your system updated and run periodic virus scans to avoid similar issues in the future. By following these solutions, you can resolve high memory and network usage, improving the overall performance of your computer.
