Fixing the “DNS Server Isn’t Responding” Issue in Windows 10
Encountering the “DNS Server Isn’t Responding” error on Windows 10 can be frustrating, as it prevents you from accessing websites and using online services. This guide provides several methods to troubleshoot and resolve this issue effectively.
Understanding the DNS Server Error
DNS (Domain Name System) servers translate domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses. When your DNS server isn’t responding, it means your device is unable to connect to the server that translates the website address into the corresponding IP address. This issue can be caused by various factors, including network configuration problems, DNS cache issues, or incorrect DNS settings.
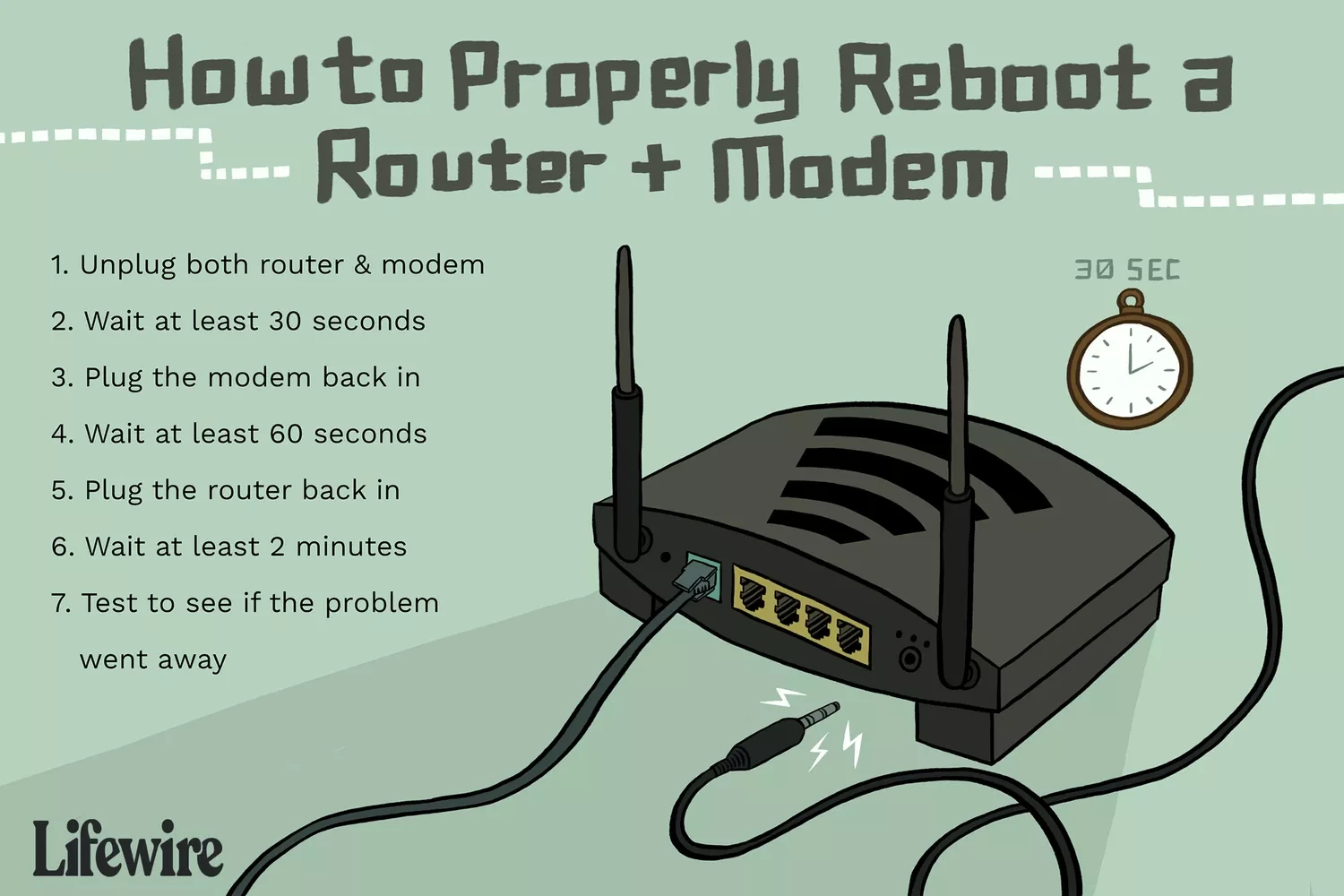
1. Restart Your Router and Computer
A simple restart of your router and computer can often resolve network-related issues.
Steps:
- Turn off your router by pressing the power button or unplugging it.
- Wait for 30 seconds, then turn it back on.
- Restart your computer by clicking on the Start menu, selecting the Power icon, and choosing Restart.
- Once both devices have restarted, check if the issue is resolved.
2. Change DNS Server Addresses
Switching to a public DNS server like Google DNS or OpenDNS can help resolve DNS-related issues.
Steps:
- Press Win + R, type ncpa.cpl, and press Enter to open Network Connections.
- Right-click your active network connection (e.g., Ethernet or Wi-Fi) and select Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
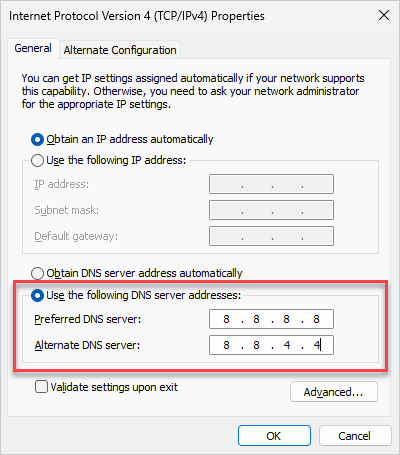
- Choose Use the following DNS server addresses and enter the following:
- Preferred DNS server:
8.8.8.8 - Alternate DNS server:
8.8.4.4
- Preferred DNS server:
- Click OK and restart your computer.
3. Flush DNS Cache
Flushing the DNS cache can resolve issues caused by corrupted or outdated DNS records.
Steps:
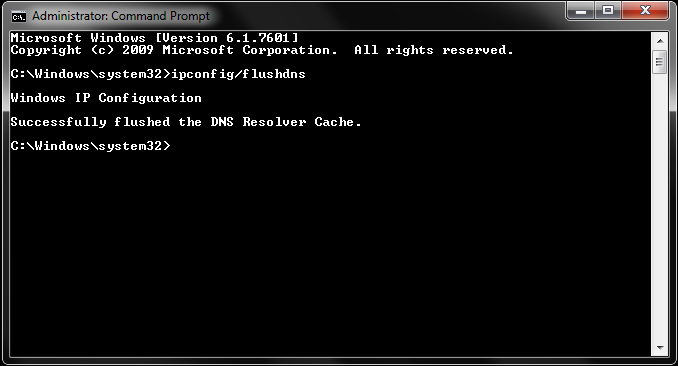
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator: Press Win + X and select Command Prompt (Admin).
- Type the following command and press Enter:
bash
ipconfig /flushdns
- You should see a confirmation message that the DNS cache has been successfully flushed.
4. Disable Additional Network Adapters
Sometimes, multiple network adapters can cause conflicts. Disabling any unnecessary adapters can help.
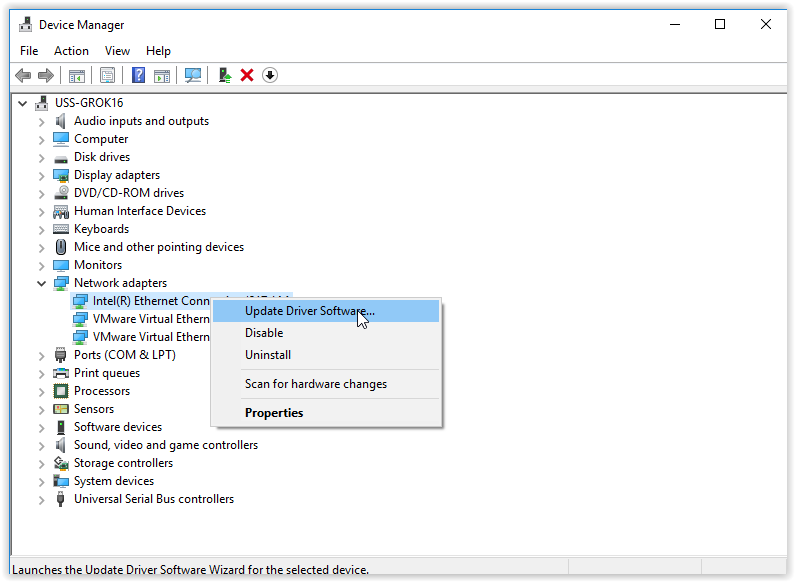
Steps:
- Open Device Manager by pressing Win + X and selecting Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters section.
- Right-click any network adapter you are not using and select Disable device.
- Restart your computer and check if the issue is resolved.

5. Reset TCP/IP Stack
Resetting the TCP/IP stack can fix issues with your network configuration.
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
perl
netsh int ip reset
netsh winsock reset
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
6. Update Network Drivers
Outdated or corrupted network drivers can cause connectivity issues. Updating your drivers can help resolve these problems.
Steps:
- Open Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters section.
- Right-click your network adapter and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for updated driver software.
- Follow the prompts to install the latest drivers.
7. Disable Antivirus/Firewall Temporarily
In some cases, antivirus software or firewalls can block your DNS server. Temporarily disabling them can help identify if they are causing the issue.
Steps:
- Open your antivirus software and disable real-time protection temporarily.
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall and turn off the firewall.
- Check if the DNS issue is resolved. Remember to re-enable your antivirus and firewall afterward.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you should be able to fix the “DNS Server Isn’t Responding” error on Windows 10 and restore your internet connectivity. Regularly updating your network drivers, maintaining your network settings, and keeping your system free of malware can help prevent such issues in the future.
